Still have questions?
Ask UpStudy online
Ask UpStudy online
-
24/7 expert live tutors
-
Unlimited numbers of questions
-
Step-by-step explanations
Ask Questions
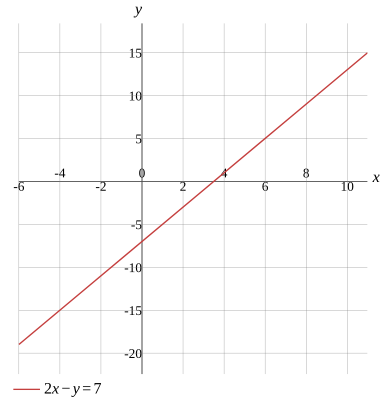
\text{Find the }x\text{-intercept/zero}
Find the y-intercept
Find the slope
\text{Solve for }x
\text{Solve for }y
Testing for symmetry about the origin
Testing for symmetry about the x-axis
Testing for symmetry about the y-axis
Rewrite in polar form
Rewrite in slope-intercept form
\text{Find the derivative with respect to }x
\text{Find the derivative with respect to }y
\text{Find the second derivative with respect to }x
\text{Find the second derivative with respect to }y
24/7 expert live tutors
Unlimited numbers of questions
Step-by-step explanations
You can enjoy